9 Steps to Carry Out Business Risk Management: Maintain Credit Stability – In the dynamic realm of business, risk is an inherent element that, if left unmanaged, can disrupt the steady pulse of an organization. Business risk management is the strategic process through which companies identify, assess, and mitigate potential risks to sustain stability and ensure long-term viability. In this article, we explore the critical role of business risk management in sustaining the pulse stability of organizations.

In the ever-evolving business landscape, uncertainty is a constant companion, making effective risk management a strategic imperative. Business risk management involves a proactive approach to identifying potential threats, understanding their impact, and implementing strategies to mitigate or capitalize on them.
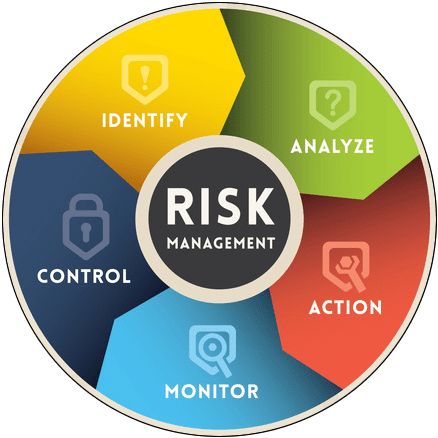
Identifying and Categorizing Risks Management: The Foundation of Management
The first step in business risk management is the identification and categorization of risks. Risks can manifest in various forms, including financial, operational, strategic, compliance, and reputational. By systematically cataloging potential risks, organizations gain a comprehensive view of the challenges they may face.
Business Risk Assessment: Understanding the Magnitude
After identification, risk assessment involves understanding the magnitude and potential consequences of each risk. This involves evaluating the likelihood of the risk occurring and the severity of its impact. By assigning a risk rating to each scenario, organizations prioritize their focus on the most critical threats.
Proactive Mitigation Strategies: Building Resilience
Proactive mitigation strategies are at the core of effective business risk management. These strategies involve developing and implementing measures to reduce the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This may include diversifying supply chains, implementing cybersecurity measures, or establishing contingency plans for potential disruptions.
Financial Risk Management: Safeguarding Assets
Financial risk management is a crucial component, focusing on safeguarding an organization’s financial assets. This includes managing currency exchange risks, interest rate fluctuations, and market volatility. By employing hedging strategies and financial instruments, organizations can mitigate the financial impact of external uncertainties.

Operational Risk Management: Ensuring Smooth Operations
Operational risk management addresses risks associated with internal processes, systems, and human factors. It encompasses measures to prevent errors, reduce inefficiencies, and enhance the reliability of operations. Robust operational risk management contributes to the overall stability and continuity of business processes. (Read More: Technology as the primary driver of business)
Compliance and Regulatory Risk: Navigating Legal Landscapes
Compliance and regulatory risks are critical considerations, especially in industries subject to strict regulations. Business risk management involves staying abreast of changes in legal landscapes, ensuring adherence to regulations, and implementing measures to mitigate the potential legal and reputational fallout of non-compliance.
Strategic Risk Management: Aligning with Objectives
Strategic risk management aligns with the broader organizational goals and involves assessing risks that could impact the achievement of strategic objectives. This includes risks related to market shifts, competition, and technological disruptions. Effective strategic risk management ensures that organizational strategies remain resilient in the face of change.
Reputational Risk Management: Guarding Brand Image
Reputational risk management focuses on safeguarding the brand image and public perception of an organization. In the age of social media and instant communication, reputational damage can occur swiftly. Strategies for managing reputational risk involve proactive communication, crisis management planning, and a commitment to ethical business practices.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: A Dynamic Process
Business risk management is not a one-time activity; it is a dynamic, ongoing process. Continuous monitoring of the risk landscape allows organizations to adapt their strategies in response to emerging threats or changing market conditions. Regular reassessment ensures that risk management practices remain relevant and effective.
Conclusion: Balancing Ambition with Prudence
In conclusion, business risk management is the art of balancing ambition with prudence, ensuring that organizations can navigate the uncertain terrain while maintaining stability. The ability to sustain the pulse stability of a business lies in its capacity to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks across various dimensions. As organizations embrace a comprehensive risk management approach, they not only protect themselves from potential pitfalls but also position themselves to seize opportunities that arise in dynamic environments. In a world where change is inevitable, effective business risk management becomes a strategic imperative for those aspiring not only to survive but to thrive in the face of uncertainty.
Read More: Time and Stress Management: Maintaining the Pulse of Professional Balance




[…] Growth Marketing Strategies Pumping Business Pulse: Fueling Growth and Visibility Business Risk Management: Sustaining the Pulse Stability Technology as the Primary Driver of Business Pulse: Navigating the Digital Era […]
[…] Growth Marketing Strategies Pumping Business Pulse: Fueling Growth and Visibility Business Risk Management: Sustaining the Pulse Stability Technology as the Primary Driver of Business Pulse: Navigating the Digital Era […]
[…] Environmental sustainability focuses on minimizing ecological impact and fostering a harmonious coexistence with the planet. Businesses are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing carbon footprints, implementing renewable energy sources, and embracing circular economy models. These initiatives not only benefit the environment but also resonate positively with environmentally conscious consumers. (Read More : Business risk management sustaining the pulse) […]
[…] Environmental sustainability focuses on minimizing ecological impact and fostering a harmonious coexistence with the planet. Businesses are increasingly adopting eco-friendly practices, such as reducing carbon footprints, implementing renewable energy sources, and embracing circular economy models. These initiatives not only benefit the environment but also resonate positively with environmentally conscious consumers. (Read More : Business risk management sustaining the pulse) […]
[…] and assessing the environmental impact of business operations is foundational for sustainability. Organizations must conduct thorough assessments to identify […]
[…] the debt-servicing ratio of Canadian households has soared to one of the highest among the advanced economies. But if longer mortgage terms had been more prevalent and attractive, the payment shock would have […]
[…] “Ours is a thermal energy storage system, storing energy as heat and dispatching as electricity. There are three core innovations to our technology, each patented. The first is our hybrid charging process, by which we charge the system first with electricity, and then in a second stage, with direct heat. The rationale for that is primarily economic,” he said. (Read More : 9 Steps to Carry Out Business Risk Management: Maintain Credit Stability Detrimental) […]
[…] Read More: 9 Steps to Carry Out Business Risk Management: Maintain Credit Stability Detrimental […]